C# Versions and Features
The C# language, developed by Microsoft in conjunction with the .NET framework, serves as a powerful programming language while .NET acts as the underlying runtime support environment. Since its initial release in 2002 alongside the .NET Framework 1.0, C# has undergone significant evolution. It's worth noting that although the C# language and its compiler are distinct entities, they still rely on the .NET framework for seamless integration. One challenge arises from C#'s versioning as it is not tightly bound to a specific version of the .NET Framework, despite synchronized releases with Visual Studio.
The C# language utilizes a standard library defined in its specification, which encompasses various types and methods. These essential features are provided by the .NET platform through multiple packages, enabling developers to utilize the rich functionality provided by the framework.

History of C# Versions
| C# Versions |
Visual Studio |
.NET Framework |
CLR version |
Year |
| Ver 1.0 |
VS 2002 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
2002 |
| Ver 1.2 |
VS 2003 |
1.1 |
1.1 |
2003 |
| Ver 2.0 |
VS 2005 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
2005 |
| Ver 3.0 |
VS 2008 |
3.5 |
2.0 |
2007 |
| Ver 4.0 |
VS 2010 |
4.0 |
4 |
2010 |
| Ver 5.0 |
VS 2012 |
4.5 |
4 |
2013 |
| Ver 6.0 |
VS 2015 |
4.6 |
4 |
2015 |
| Ver 7.0 |
VS 2017 |
4.7 |
4 |
2017 |
| Ver 8.0 |
VS 2019 |
4.8 |
4 |
2019 |
C# Versions and Features
| C# Versions |
Visual Studio |
.NET Framework |
CLR version |
Year |
| Ver 1.0 |
VS 2002 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
2002 |
- Classes
- Structs
- Interfaces
- Events
- Properties
- Delegates
- Expressions
- Statements
- Attributes
- Literals
| C# Versions |
Visual Studio |
.NET Framework |
CLR version |
Year |
| Ver 1.2 |
VS 2003 |
1.1 |
1.1 |
2003 |
- Dispose in foreach
- foreach over string specialization
| C# Versions |
Visual Studio |
.NET Framework |
CLR version |
Year |
| Ver 2.0 |
VS 2005 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
2005 |
- Generics
- Partial types
- Anonymous methods
- Iterators
- Nullable types
- Getter/setter separate accessibility
- Method group conversions (delegates)
- Static classes
- Delegate inference
| C# Versions |
Visual Studio |
.NET Framework |
CLR version |
Year |
| Ver 3.0 |
VS 2008 |
3.5 |
2.0 |
2007 |
- Implicitly typed local variables
- Object and collection initializers
- Auto-Implemented properties
- Anonymous types
- Extension methods
- Query expressions
- Lambda expression
- Expression trees
- Partial methods
| C# Versions |
Visual Studio |
.NET Framework |
CLR version |
Year |
| Ver 4.0 |
VS 2010 |
4.0 |
4 |
2010 |
- Dynamic binding
- Named and optional arguments
- Co- and Contra-variance for generic delegates and interfaces
- Embedded interop types ("NoPIA")
| C# Versions |
Visual Studio |
.NET Framework |
CLR version |
Year |
| Ver 5.0 |
VS 2012 |
4.5 |
4 |
2013 |
- Asynchronous methods
- Caller info attributes
| C# Versions |
Visual Studio |
.NET Framework |
CLR version |
Year |
| Ver 6.0 |
VS 2015 |
4.6 |
4 |
2015 |
- Draft Specification online
- Compiler-as-a-service (Roslyn)
- Import of static type members into namespace
- Exception filters
- Await in catch/finally blocks
- Auto property initializers
- Default values for getter-only properties
- Expression-bodied members
- Null propagator (null-conditional operator, succinct null checking)
- String interpolation
- nameof operator
- Dictionary initializer
| C# Versions |
Visual Studio |
.NET Framework |
CLR version |
Year |
| Ver 7.0 |
VS 2017 |
4.7 |
4 |
2017 |
- Out variables
- Pattern matching
- Tuples
- Deconstruction
- Discards
- Local Functions
- Binary Literals
- Digit Separators
- Ref returns and locals
- Generalized async return types
- More expression-bodied members
- Throw expressions
| C# Versions |
Visual Studio |
.NET Framework |
CLR version |
Year |
| Ver 8.0 |
VS 2019 |
4.8 |
4 |
2019 |
- Nullable reference types
- Default interface members
- Recursive patterns
- Async streams
- Enhanced using
- Ranges and indexes
- Null-coalescing assignment
- Static local functions
- Unmanaged generic structs
- Readonly members
- Stackalloc in nested contexts
- Alternative interpolated verbatim strings
- Obsolete on property accessors
How to target different C# version in Visual Studio 2019
- Open the project properties window (right click on project, select properties)
- Select "Build" from the left hand side options
- Scroll down to the Advanced options
- Select the desired version of C#, click ok
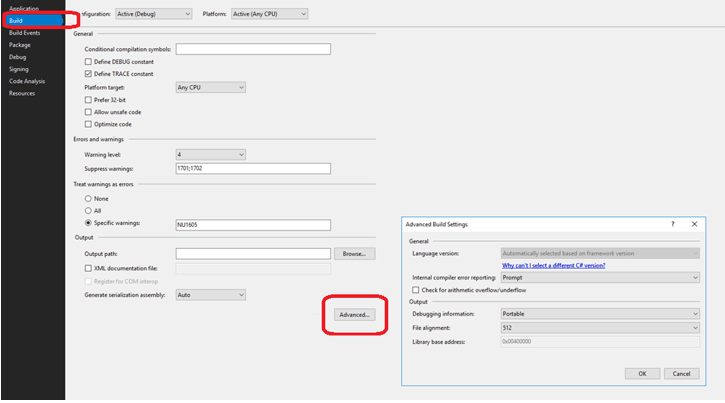
The latest C# compiler determines a default language version based on your project's target framework(s). This is because the C# language may have features that rely on types or runtime components that are not available in every .NET implementation . The rules in this article apply to the compiler delivered with Visual Studio 2019 , or the .NET Core 3.0 SDK.
| Target framework |
Version |
C# language version |
| .NET Core |
3.x |
C# 8.0 |
| .NET Core |
2.x |
C# 7.3 |
| .NET Standard |
2.1 |
C# 8.0 |
| .NET Standard |
2.0 |
C# 7.3 |
| .NET Standard |
1.x |
C# 7.3 |
| .NET Framework |
all |
C# 7.3 |

One thing you should be aware that the C# compilers that are part of the Visual Studio 2017 installation or earlier .NET Core SDK versions target C# 7.0 by default.


